Appearance
服务器只对html文件不缓存、缓存build打包js,css等文件带上时间戳(html引入更新及时)
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
#add_header X-Via $server_addr;
#要缓存文件的后缀,可以在以下设置。
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|png|jpeg|css|js)(.*) {
#对不同的HTTP状态码设置不同的缓存时间
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:90;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache cache_one;
#以域名,URI,参数组合成web缓存的key值,nginx根据key值哈希
proxy_cache_key $host$uri$is_args$args;
# 为不同的响应状态码设置不同的缓存时间
#proxy_cache_valid 200 10s;
proxy_cache_valid any 100s; #缓存文件过期时间,未过期则304,过期则200重新访问缓存
expires 30s; #浏览器端看到的max-age以及expires的值,前端根据这个决定是否请求服务器
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status";
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:90;
}
}
server {
listen 90;
listen [::]:90;
root /var/www/not_save/;
index index.html;
location / {
# 配置页面不缓存html和htm结尾的文件
if ($request_filename ~* .*\.(?:htm|html)$) {
add_header Cache-Control "private, no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
}
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html =404;
}
}当nginx设置了expires后,例如设置为:expires 10d; 那么用户在10天内请求的时候,都只会访问浏览器中的缓存,而不会去请求nginx。
Response Headers
- cache-Control: max-age="过期所需时间/秒"
- Expires:表示具体过期时间
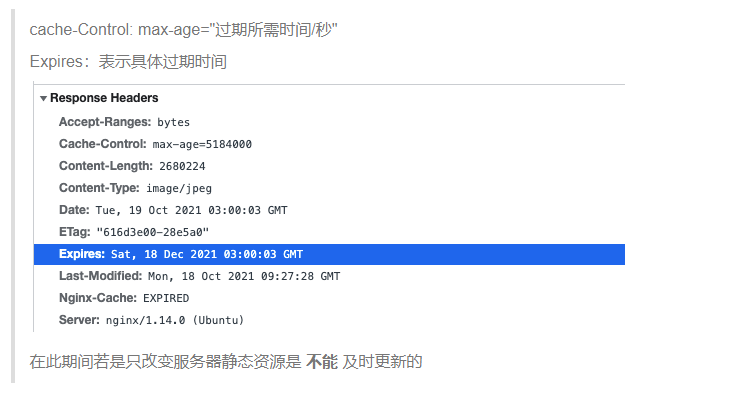
在此期间若是只改变服务器静态资源是 不能 及时更新的
第一次访问
访问资源,直接下载  服务器静态资源缓存文件
服务器静态资源缓存文件 
第二次访问(Expires缓存未过期)
直接刷新页面 memory cache 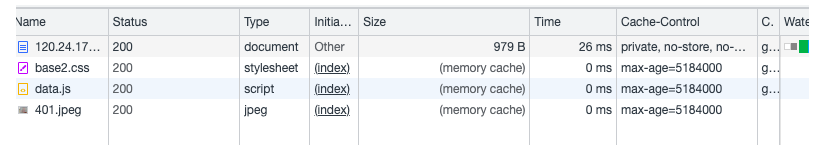
- 200 form memory cache 内存缓存
不访问服务器,一般已经加载过该资源且缓存在了内存当中,直接从内存中读取缓存。浏览器关闭后,数据将不存在(资源被释放掉了),再次打开相同的页面时,不会出现from memory cache。
关闭浏览器再打开 disk cache 
- 200 from disk cache 硬盘缓存
不访问服务器,已经在之前的某个时间加载过该资源,直接从硬盘中读取缓存,关闭浏览器后,数据依然存在,此资源不会随着该页面的关闭而释放掉下次打开仍然会是from disk cache。
第二次访问(Expires缓存已过期)
等到expires过期后再刷新,确认服务器缓存过期则重新访问后台数据并返回200,未过期则304 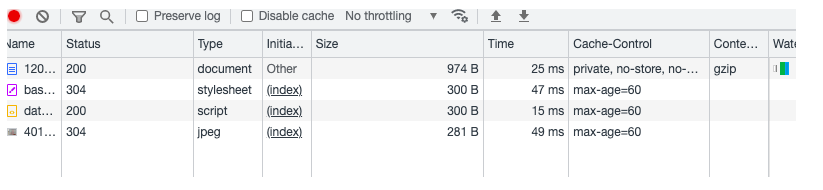
- 304 Not Modified
访问服务器,发现数据没有更新,服务器返回此状态码。然后从缓存中读取数据。
强制更新(Expires无论过期否,html引入静态资源变更)
- 前端webpack打包build,html的文件,html前端是禁止缓存的,服务器也没有缓存,所以会直接返回最新的html文件读取最新静态文件
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status"
MISS 未命中,请求被传送到后端
HIT 缓存命中
EXPIRED 缓存已经过期请求被传送到后端
UPDATING 正在更新缓存,将使用旧的应答
STALE 后端将得到过期的应答Expires
expires 30s; #缓存30秒
expires 30m; #缓存30分钟
expires 2h; #缓存2小时
expires 30d; #缓存30天缓存具体类型
cache-control: max-age=xxxx,public
客户端和代理服务器都可以缓存该资源;
客户端在xxx秒的有效期内,如果有请求该资源的需求的话就直接读取缓存,statu code:200 ,如果用户做了刷新操作,就向服务器发起http请求cache-control: max-age=xxxx,private
只让客户端可以缓存该资源;代理服务器不缓存
客户端在xxx秒内直接读取缓存,statu code:200cache-control: max-age=xxxx,immutable
客户端在xxx秒的有效期内,如果有请求该资源的需求的话就直接读取缓存,statu code:200 ,即使用户做了刷新操作,也不向服务器发起http请求cache-control: no-cache
跳过设置强缓存,但是不妨碍设置协商缓存;一般如果你做了强缓存,只有在强缓存失效了才走协商缓存的,设置了no-cache就不会走强缓存了,每次请求都回询问服务端。cache-control: no-store
不缓存,这个会让客户端、服务器都不缓存,也就没有所谓的强缓存、协商缓存了。max-age: 相对过期时间, 即以秒为单位的缓存时间.
- private, 正数的max-age: 后退时候不会访问服务器.
- no-cache, 正数的max-age: 后退时会访问服务器.must-revalidate
缓存必须在使用之前验证旧资源的状态,并且不可使用过期资源。表示如果页面过期,则去服务器进行获取。proxy-revalidate
与must-revalidate作用相同,但它仅适用于共享缓存(例如代理),并被私有缓存忽略。
实例Demo
# 正向代理-测试地址
server {
listen 80;
server_name qy.hlgshare.top;
root /home/vite2-vue3-qingyuan;
location ~* ^.+\.(css|js|txt|xml|swf|wav|gif|jpg|png|jpeg)$ {
add_header Cache-Control max-age=2592000; #30天
add_header Cache-Control public; #前后端都可以缓存
}
location / {
if ($request_filename ~* .*\.(?:htm|html)$) { # 对html不缓存
add_header Cache-Control "no-cache, no-store";
add_header Pragma no-cache;
add_header Expires 0;
}
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html;
index index.html;
}
}
# 反向代理-测试地址
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name _;
#add_header X-Via $server_addr;
#要缓存文件的后缀,可以在以下设置。
location ~ .*\.(gif|jpg|png|jpeg|css|js)(.*) {
#对不同的HTTP状态码设置不同的缓存时间
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:90;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache cache_one;
#以域名,URI,参数组合成web缓存的key值,nginx根据key值哈希
proxy_cache_key $host$uri$is_args$args;
# 为不同的响应状态码设置不同的缓存时间
#proxy_cache_valid 200 10s;
proxy_cache_valid any 2592000s; #缓存文件过期时间,未过期则304,过期则200重新访问缓存
expires 360s; #浏览器端看到的max-age以及expires的值,前端根据这个决定是否请求服务器
add_header Nginx-Cache "$upstream_cache_status";
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:90;
}
}
server {
listen 90;
listen [::]:90;
root /home/vite2-vue3-qingyuan-reverse;
index index.html;
location / {
# 配置页面不缓存html和htm结尾的文件
if ($request_filename ~* .*\.(?:htm|html)$) {
add_header Cache-Control "private, no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, proxy-revalidate";
}
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html =404;
}
}